Web 3.0 responds to many of the pressures of modern times such as power being concentrated in the hands of small groups of people. People are rapidly losing faith in large organisations — from corporations to charities — due to a lack of transparency and democracy. This is why blockchain technology is now being leveraged to create DAOs.
What are DAOs?
DAOs, or Decentralised Autonomous Organizations, use blockchain technology to run and make decisions. In traditional organisations, decisions are made top-down, such as by a board of directors. In a DAO, all token-holding community members get to vote on its decisions. Using smart contracts, they can vote on how funds are used and what projects to pursue. This means that both ownership and decision-making of the organization are decentralized. This ensures the decisions made reflect the community’s interests and values rather than only those of the people at the top. The organization is thus freed from the control and corruptibility of a single central authority.
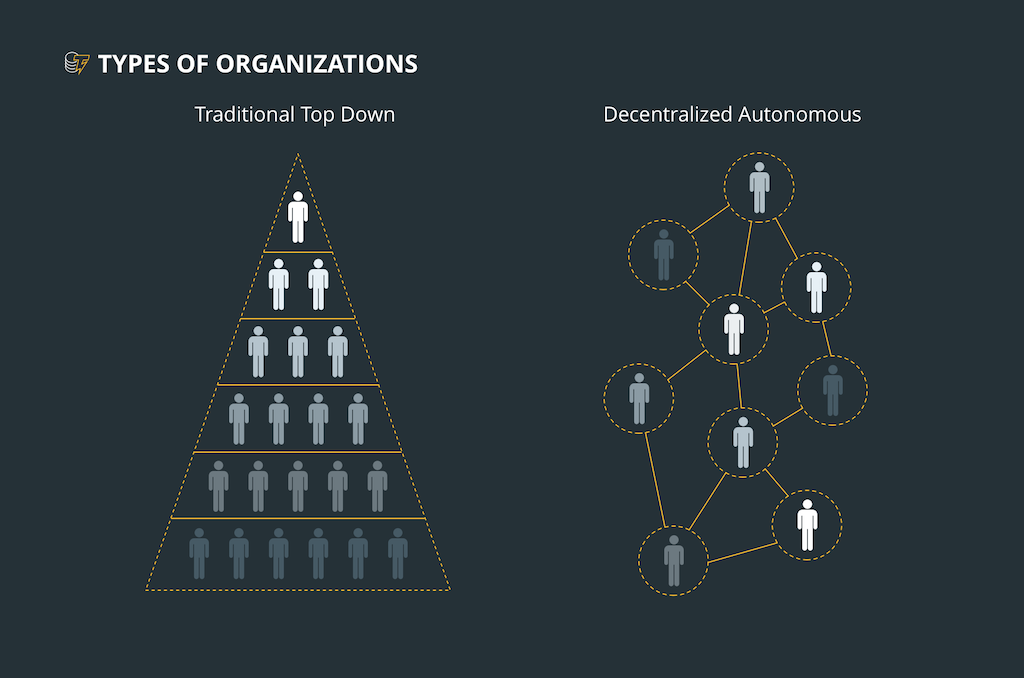
DAOs are automated using smart contracts — pieces of self-executing code stored on the blockchain. The rules for the DAO (who can vote, how many votes to pass a proposal etc.) are stored in these smart contracts. Instead of people interpreting and executing rules, the smart contract does it all. This makes the process of governance straightforward, instant, and tamper-proof. There is little room for human error or tampering and little need for time-consuming bureaucracy.
Smart contract data is stored forever on an uneditable blockchain. This means there is a transparent, public ledger permanently available recording the workings of the DAO. Anyone with the appropriate access can use this to hold the DAO accountable. This level of transparency is new and fosters a sense of trust within the community that old organizations lack.
Use Cases
DAOs are revolutionary in how they allow a community to mobilize, fund, and direct itself. They are being used in innovative ways in diverse industries to achieve various goals.
Venture Capital Funds
VC DAOs allow people to pool money together and fund projects such as business ventures and dApp development. This opens up VC funding to ordinary people eliminating barriers to entry such as the need for capital, geography etc. In short, VC DAOs help democratize funding and investment.
Voting ensures the projects pursued align with the goals and values of the community that funds them. Blockchain’s transparency and security mean little risk of funds being misused or misappropriated.
Crowdfunding
Think Patreon, but one step further. Patreon created the subscription-based model that allows ordinary people to fund creators and projects independently. DAOs allow the same kind of funding, but also give people the ability to make decisions about the project. Whether this means funding a new videogame or a community centre is up to the token holders. Integration with other Web 3.0 technologies such as NFTs also creates a reward system for those who fund projects.
Raising Charitable Funds
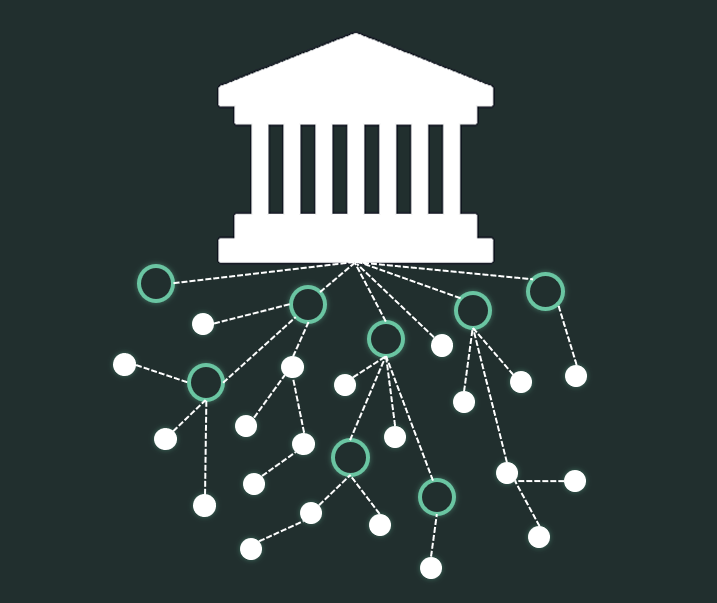
This decentralized model also allows for a different approach to charity. Instead of large organizations controlling funds and their use, DAOs create a more grassroots approach. Rather than relying on external help, communities can raise, control, and distribute funds independently and democratically. This empowers communities to use their understanding of their own issues to create the solutions that fit them best. Unprecedented trust can be created through the transparency offered by a DAO.
Click here to find out how we at NoCap Meta are using blockchain technology to make the world a better place.
Metaverse and dApp Governance
For Web 3.0 ventures, decentralization is more than a buzzword — it is a core value. This is why more and more Web 3.0 native companies (Metaverse and dApp creators for example) are shifting to the DAO governance model. This means their platforms will be built with the community’s needs at the forefront. It also creates a sense of community and ownership that makes the venture collaborative and social rather than just economic.

The Road Ahead
There are still several challenges facing DAOs in the real world. Firstly, the level of technical expertise involved in setting up a DAO and its smart contracts can be a barrier to entry. But, as the world at large shifts towards Web 3.0 and more developers crop up, this will resolve itself.
Then, there is the issue that voting is tied to holding tokens. It remains up to the creators of the DAO to ensure that the token price and number of tokens required to vote do not compromise its diversity and decentralization.
And although smart contracts are great at enforcing their rules, vulnerabilities in the initial contract can compromise security. Every new technology has a learning curve, and learning how to create watertight smart contracts will be a part of this.
DAOs are still a nascent technology and don’t have the benefit of experience that traditional organizations do. However, the values they make possible — decentralization, transparency, and community — are important. Given time and investment, DAOs have the potential to transform commerce and culture.

